What is the NBN?
The National Broadband Network, or NBN for short, is a high speed broadband network that’s being rolled out by the Australian Government owned NBN (formerly NBN Co.)
The NBN is in charge of providing high-speed broadband connections to every home and office in Australia. It is also giving telephone and internet service providers’ access to the NBN so they can deliver services like telephony, entertainment, security and e-health to homes and businesses.
To make this happen, the NBN is using a range of broadband technologies, including:
- Fibre to the premises or FTTP
- Fibre to the building or FTTB
- Fibre to the node or FTTN
- HybridFibre Coax (HFC) or more commonly known as Pay TV cable
- Fixed wireless
- Satellite
For most people only the first three options will be important. However any NBN connection means thinking about where your internet equipment is installed in your home or office so the faster broadband speeds work properly wherever you are in the building.
No matter which type of technology is used to deliver the NBN it’s crucial the home and office wiring has been well planned. If you are cabling a new or renovated home the most important principle is that all cabling should be “star wired Cat 6 cable” from a central location where the NBN equipment will ideally be installed. This star wired cat 6 cabling you have installed can be used to connect telephone, computers, PC, laptops and even WiFi devices where you need them.
FTTP
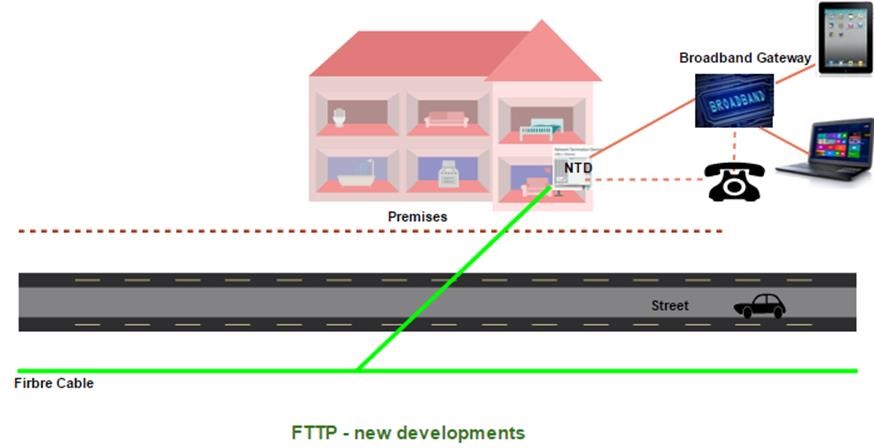
FTTP is Fibre To The Premises, where fibre is run into your home and terminated on a device supplied by NBN called Network Termination Device (NTD for short). It allows you to have up to 2 different phone service providers and 4 different data service providers.
There are 2 sorts of FTTP rollouts. One is in new estates where fibre is the only technology installed to provide telephone and internet services to every home.
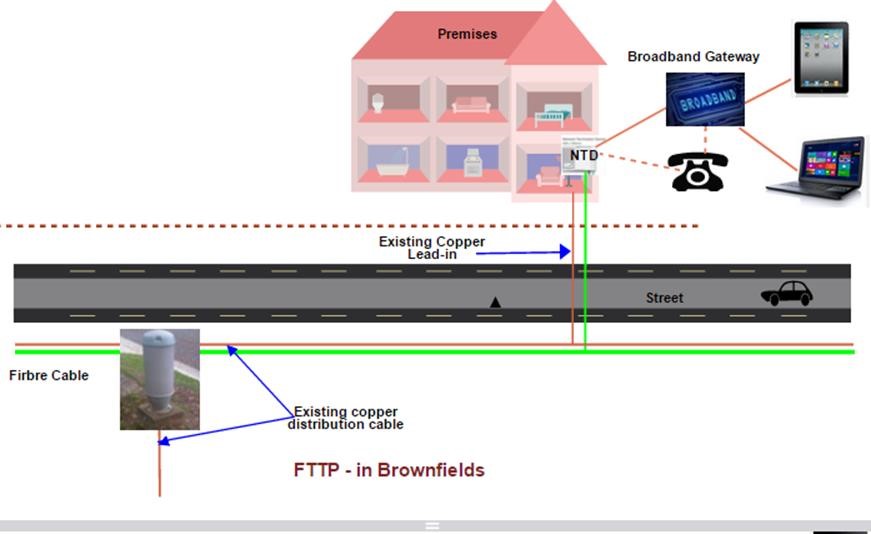
The other one is in existing suburbs. Here the fibre being installed piggybacks on the existing copper telephone network.
FTTB
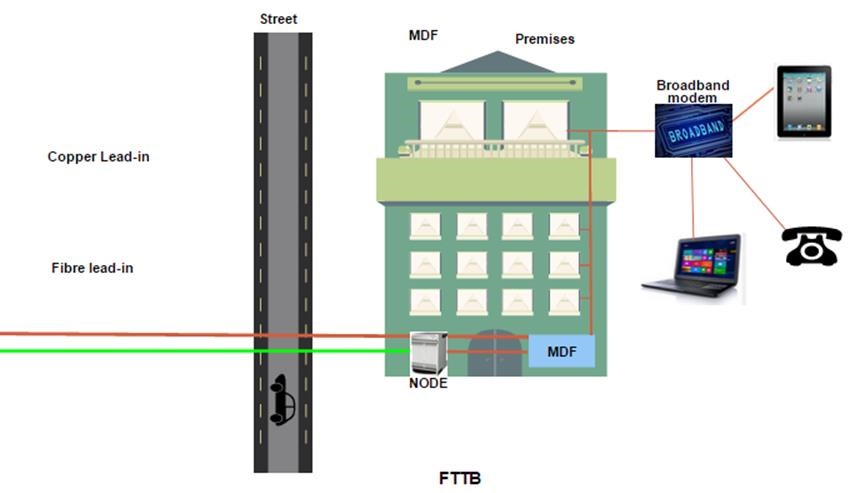
FTTB is where fibre is installed to a building or apartment complex. It terminates at a node that converts the optical signal into one suitable for the existing copper cable in order to ’extend’ the broadband service to all apartments or offices.
The technology that helps this occur over the copper telephone wire is called VDSL, a faster version than the more common ADSL broadband. The VDSL modem will be very similar to the existing ADSL modems.
FTTN
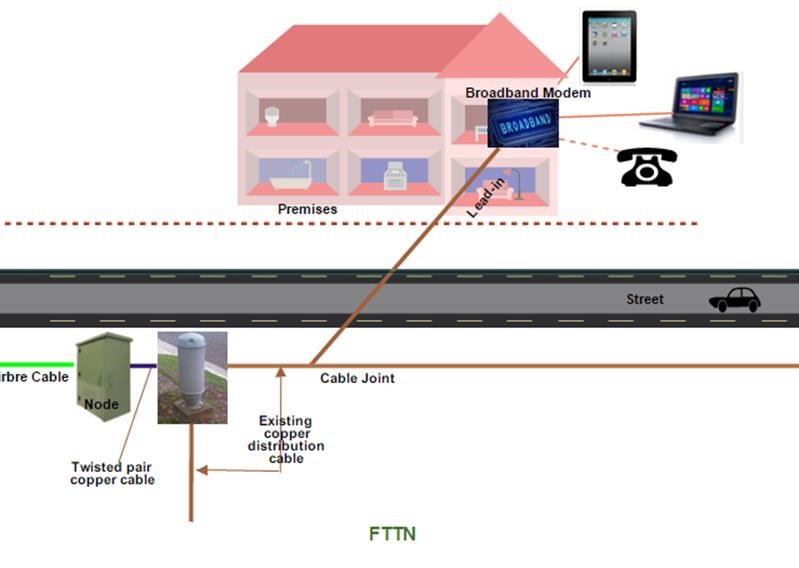
FTTN, or Fibre To The Node, is like FTTB except the node is installed outside the premises so it can service multiple premises. The ideal location would be next to an existing telecommunications pillar.
The technology from the node to the Multiple Dwelling Unit (apartment building, townhouses, etc) or Single Dwelling Unit (freestanding house) is VDSL. The connection and installation inside the dwelling will be the same as for ADSL. The node needs to be reasonably close to the dwelling so the copper length is kept as short as possible.
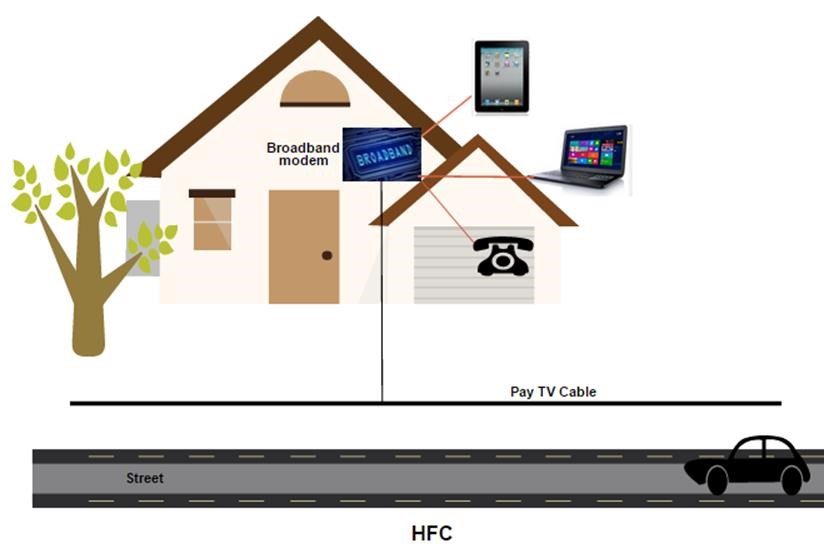
HFC
HFC is where high speed broadband is delivered over the existing pay TV network so the installation inside the home is the same as the existing cable modem. Using the latest technology it is possible to deliver both broadband and telephony from the cable modem.
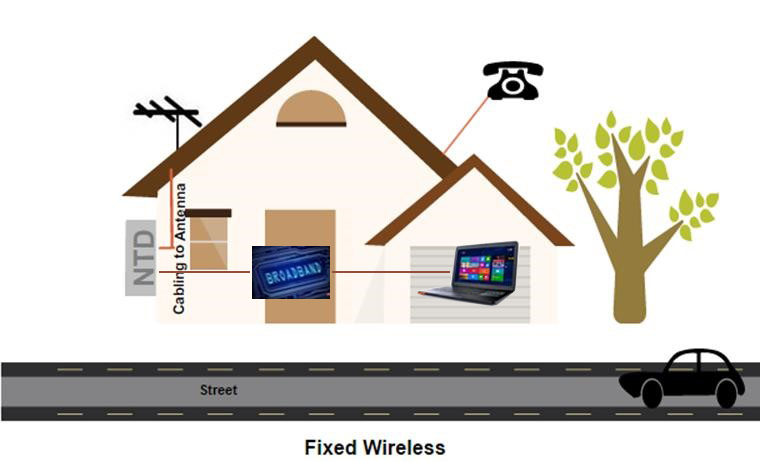
Fixed wireless
Fixed wireless is where NBN will install radio base stations like the ones used for mobile phones and then install an antenna and a fixed modem (NTD) in the premises. This NTD is only for broadband service, the telephony stays on the existing copper wires for now.
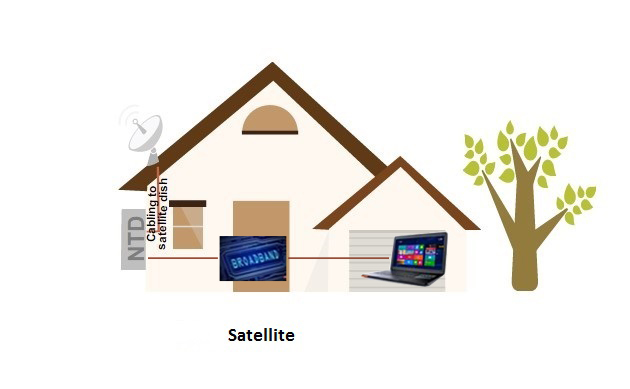
Satellite
The NBN is also using satellites to cover remote areas, installing a satellite dish connected to an NTD. Like fixed wireless this NTD will provide broadband services only.
Have you been missing out? Don’t forget to list your business on our site!
